Celix Cellulose Co., Ltd, is an integrated chemical cellulose manufacturer with in-house R&D, factories, and global sales sites.
Our products include HPMC, HEC, MHEC, VAE RDP, PCE, PVA, Defoamers, PP fibers, HPS, SHP and Gypsum Retarder.

| Specification | Index |
| Exterior | White or light yellowish white |
| Dosage,% | 0.8-1.2 |
| Viscosity(Brookfield, 2%, 20°C, mpa.s) | 400-75000 |
| Moisture content,% | ≤5 |
| Particle Size | 100-120 mesh |
| pH Value | 6-8 |

Film Formation
Enzyme Resistance

Water Retention

Surface Activity

Pseudoplasticity

PH Stability

Thickening & Binding
The production process of HEC (hydroxyethyl cellulose) typically involves three main steps: alkalization, etherification, and post-treatment.
First, refined cellulose (such as wood pulp) is alkalized under alkaline conditions to produce alkaline cellulose.
Next, the alkaline cellulose undergoes an etherification reaction with ethylene oxide in the presence of a catalyst, introducing hydroxyethyl side chains. Finally, post-treatment, including neutralization, washing, filtration, centrifugation, and drying, yields the final HEC product.
During the manufacturing process, the factory launched:
1. Real-time monitoring DCS System: to protect viscosity, substitution, and consistency.
2. Quality Control: starts with the meticulous selection of raw materials extending throughout the whole production process.
Celix Hydroxyethyl Cellulose HEC could offer:
1. Good Film formation
2. Good Enzyme resistance
3. High Water retention
4. Perfect Surface activity
5. Pseudoplasticity
6. Good PH stability
7. Good Thickening & Binding Effect
The advanced testing techniques, like IR and GPC, provide trust in every batch by ensuring consistent product quality and dependable performance.
It is used as the thickener, stabilizer in coatings, detergents, oil drilling; Sometimes, it is also used in the pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.
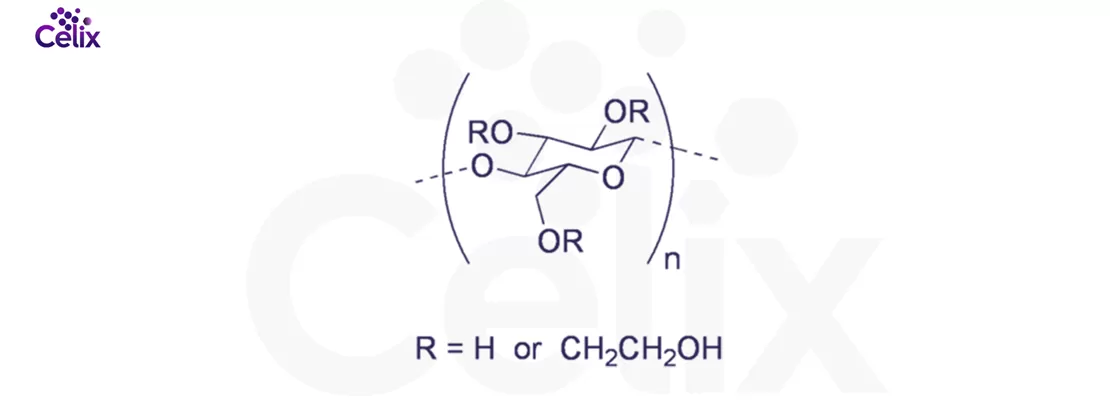
HEC material is a hydroxyethyl cellulose, a non-ionic cellulose ether with water-soluble, thickening properties.
HEC cellulose is a hydroxyethyl cellulose, made by etherifying natural cellulose with ethylene oxide.
HEC has hydroxyethyl groups; HPMC has methyl + hydroxypropyl groups. HPMC has the better thermal stability.
It's avg hydroxy groups substituted by hydroxyethyl per glucose unit (0.5–1.5 industrially, max 3 theoretically).The specific value affects its thickening properties, water retention and application areas. For example, high substitution degree is often used for coating thickening, while low substitution degree is suitable for textile processing, etc.
RECOMMENDED PRODUCTS
Contact Us

Celix Cellulose Co., Ltd, is an integrated chemical cellulose manufacturer with in-house R&D, factories, and global sales sites.
Our products include HPMC, HEC, MHEC, VAE RDP, PCE, PVA, Defoamers, PP fibers, HPS, SHP and Gypsum Retarder.